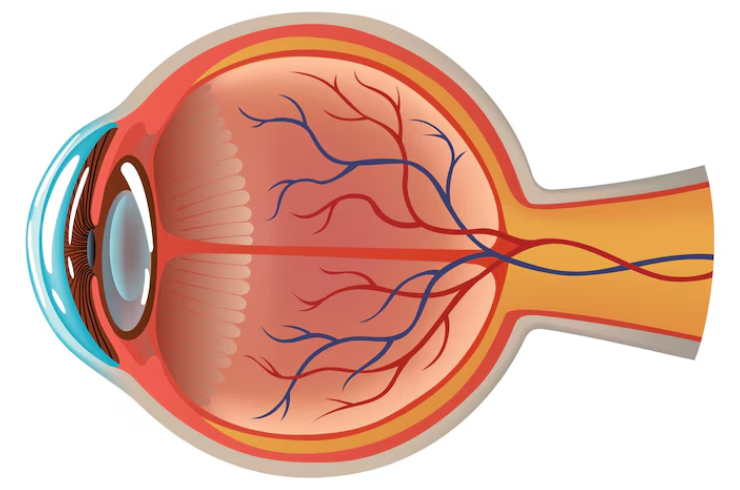
The retina is a vital layer of tissue located at the back of the eye, responsible for capturing light and converting it into electrical signals that are sent to the brain, enabling vision. Retinal health is crucial, as the retina plays a central role in our visual system.
Description and Significance
Retinal diseases can be linked to various systemic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia (cholesterol issues), and renal problems. Our retina specialists employ state-of-the-art imaging techniques, including Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiography, to achieve precise diagnoses. Treatment options are tailored to each patient and may include topical drops, antioxidant medications, and intravitreal injections. Early detection and prompt intervention are essential to preserve vision and prevent further complications. For complex cases, vitrectomy may be performed to facilitate visual rehabilitation.
Highlights and Unique Hospital Features
Our team specializes in managing conditions such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy, utilizing advanced imaging technologies for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. We are renowned for our expertise in retinal care, offering minimally invasive vitrectomy procedures for effective treatment. With leading retina specialists on staff, we ensure top-notch care for all retinal conditions, aiming to preserve and restore optimal vision for our patients.
The retina is the innermost layer of the eye that contains light-sensitive cells called photoreceptors. Its primary function is to capture light and convert it into electrical signals that are sent to the brain, allowing us to see.
Common retinal conditions include age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, and retinal vascular diseases. Symptoms may include blurry or distorted vision, floaters, flashes of light, and loss of peripheral vision.
A retinal detachment occurs when the retina separates from the underlying tissue. Signs include sudden flashes of light, an increase in floaters, and a curtain-like shadow in the visual field. Immediate medical attention is crucial.
AMD is a condition where the macula, a small part of the retina responsible for central vision, deteriorates. Treatment options may include lifestyle changes, medications, or procedures like anti-VEGF injections
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that affects the blood vessels in the retina. Management may involve controlling blood sugar levels, regular eye exams, and in some cases, laser therapy or injections.
A retinal tear or hole can be treated with a procedure called retinal laser photocoagulation or with a freezing treatment called cryopexy. , depending on the stage and condition , vitrectomy and ERM peeling. These treatments help to prevent the progression to a retinal detachment.
Yes it can be and they have to be screened once in 6 months
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and certain vitamins and minerals can support retinal health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and protecting the eyes from excessive UV exposure can be beneficial