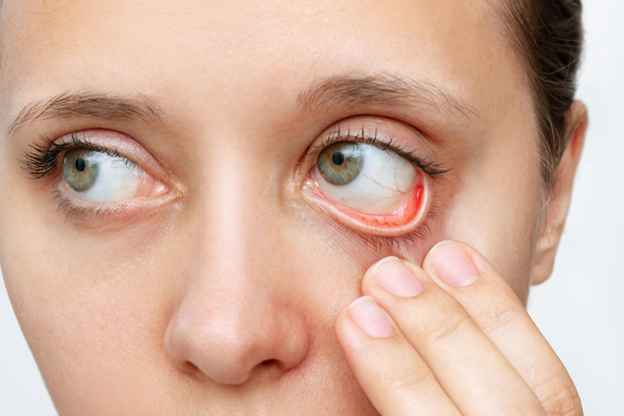
What is Uveitis?
Uveitis is when the uvea, the part of the eye that sits between the retina and the white of the eye, gets inflamed. This inflammation can affect one or both eyes and can lead to discomfort and vision issues.
Symptoms of Uveitis
Uveitis can cause various symptoms, which might differ depending on which part of the uvea is inflamed. Common signs include:
- Eye Pain: Aches or discomfort in the eye.
- Redness: The eye or the surrounding area looks red.
- Blurred Vision: Difficulty seeing clearly.
- Light Sensitivity: Pain or discomfort when looking at bright lights.
- Floaters: Seeing spots or shadows in your vision.
- Vision Loss: In severe cases, you might experience a sudden drop in vision.
What Causes Uveitis?
Uveitis can have several causes, including:
- Infections: Bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites can cause inflammation in the eye.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions where the body’s immune system attacks itself, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, can lead to uveitis.
- Eye Injury: Trauma or injury to the eye can result in inflammation.
- Systemic Diseases: Diseases like Behçet’s disease or sarcoidosis, which affect the whole body, can also cause uveitis.
- Unknown Causes: Sometimes, no specific cause is found, which is called idiopathic uveitis.
How is Uveitis Diagnosed?
If you think you might have uveitis, your doctor will perform a thorough eye exam. This includes:
- Medical History: Talking about your symptoms, recent illnesses, or any eye injuries.
- Eye Exam: Checking for signs of inflammation and assessing your vision.
- Special Tests: You might need blood tests, imaging scans, or other exams to find out what’s causing the inflammation and check for other health issues.
Treatment for Uveitis
Treating uveitis focuses on reducing inflammation, managing symptoms, and addressing any underlying causes. Common treatments include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs like corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation. These might be eye drops, oral pills, or injections.
- Dilating Eye Drops: These can ease pain and prevent complications by relaxing the muscles in the eye.
- Antibiotics or Antivirals: If an infection is causing the uveitis, your doctor might prescribe medications to treat it.
- Immunosuppressive Drugs: For autoimmune-related uveitis, drugs that suppress the immune system might be used.
Living with Uveitis
To manage uveitis, regular check-ups with an eye specialist are important to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed. Following your doctor’s advice and taking medications as prescribed can help you manage symptoms and maintain your eye health.
Uveitis is a serious eye condition, but with prompt treatment, most people can manage it effectively. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options will help you work with your doctor to keep your eyes healthy and preserve your vision. If you have symptoms of uveitis, seek medical advice right away to get the care you need.